by Jim Hodgson
With all of my passion for justice and in the face of so many gross injustices, I can get paralyzed. And with Trump in power next door, there is always something new to distract us from what went before or from demanding freedom for captives or the release of the #EpsteinFiles.
Just today, he threatened Canada again. #ElbowsUp, still.
Yesterday, it was a plan to end Israel’s war in Gaza that even the New York Times admits “checks every box on Israel’s wish list.” It does nothing to strengthen Palestine or assist recovery after the genocide, and will impose a new, colonial-style authority on the people.
Let’s step back for a moment.
Last week, I was going to write about Trump’s efforts to rescue his far-right cronies in Argentina and Brazil. Here’s a short version.
Argentina’s president, Javier Milei, faces a collapsing peso and political setbacks. Milei’s chainsaw approach to slashing government was a model for Trump and Elon Musk. U.S. Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent said Sept. 22 that Washington is ready to do “whatever is necessary” – from central bank swaps to direct peso purchases or buying Argentine debt through the Treasury’s Stabilization Fund. The moves are intended to ease political opposition to Milei that has grown as the economy collapses. Milei – already dependent on a $20 billion IMF package – sought U.S. support ahead of congressional elections in October. Investors have been pulling money out from Argentina since Milei’s party lost an election in Buenos Aires province on Sept. 7, provoking worry that he will soon lack legislative support to advance his agenda.

Earlier, Trump imposed a 50% tariff on goods from Brazil, claiming that Brazil engages in unfair trade practices and that the government is engaged in a “witch hunt” against Trump’s ally, former president Jair Bolsonaro. Bolsonaro was convicted earlier this month of attempting a coup after voters dumped him from office. He was sentenced to more than 27 years in prison, sparking Trump’s ire. The present Brazilian government called the U.S. move “a new attempt of undue interference in Brazilian internal affairs.”
When he spoke of the U.S. rescue of Argentina’s Milei, Bessent told reporters that the Trump administration hoped to solidify what it sees as a rightward shift in Latin American countries, including potentially Colombia. (Colombia is now government by a left-centre coalition led by President Gustavo Petro, who cannot succeed himself. His party is currently selecting a new candidate.)
New and old threats
Bessent’s move came hours before Trump took centre stage at the United Nations General Assembly to press his MAGA-style policies on the rest of the world.

In the speech, Trump threatened to “blow out of existence” Venezuela’s president, Nicolás Maduro. Maduro responded with a plan to declare a state of external unrest to enable rapid mobilization in defence of Venezuela. He had earlier sent a letter to Trump, proposing direct talks. When asked about the letter, White House press secretary Karoline Leavitt, said it was “full of lies” and said the administration still views Maduro as an “illegitimate leader.”
Trump’s threat came after he moved warships into the south Caribbean and after recent attacks on Venezuelan fishing boats (alleged without evidence to be carrying drugs). Trump and his minions seem determined to revive the worst applications of U.S. foreign policy in Latin America, from the 19th-century Monroe Doctrine to Teddy Roosevelt’s “big-stick” diplomacy in the early 20th century.
A recent US government document revealed the Trump administration plans to redirect $1.8 billion in foreign aid toward a new “America First” strategy, Reuters news agency reported Sept. 24. It would give priority to neutralizing “Marxist, anti-American regimes” in Latin America. The report said $400 million would support activities to end illegal immigration to the US, counter China, and “confront the Marxist, anti-American regimes of Venezuela, Cuba and Nicaragua.” The document, known as a Congressional Notification, follows news that the upcoming National Defense Strategy will also pivot the U.S. away from a focus on adversaries like China and Russia to instead prioritize efforts in the Americas.
But not everyone serving Trump is onside with these approaches. On Sept. 29, the Washington Post reported that eight current and former officials have said there is a deep rift between the political appointees at the Pentagon and the military leaders there. Reflecting on the Post report, historian Heather Cox Richardson said that War Secretary Pete Hegseth “is withdrawing forces from Europe, reducing the concentration of power and consolidating commands abroad while focusing on using the military in the U.S. and neighboring countries.“
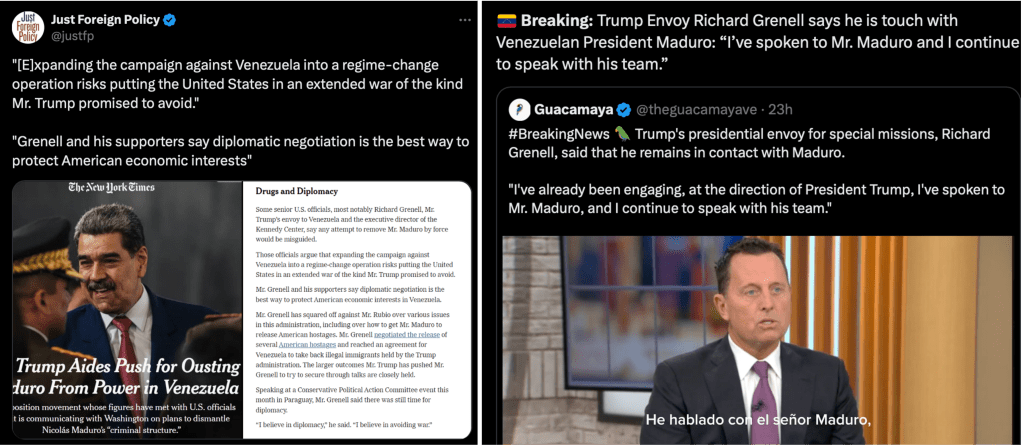
Among Trump administration opponents to use of force to provoke regime change in Venezuela is Richard Grenell, Trump’s special envoy to the country, said Drop Site News on Sept. 29. Grenell has successfully re-opened channels for export of Venezuelan oil to the United States. Grenell and his supporters say diplomatic negotiation is the best way to protect U.S. economic interests. Among those who oppose Grenell is U.S. Secretary of State Marco Rubio.





