by Jim Hodgson
“American inauguration day was a grim business, like someone slamming a baseball bat into the concept of human decency all day long until it was bleeding and paper-thin,” wrote Heather Mallick today in the Toronto Star.
In a blizzard of speeches, insults and executive orders, Donald Trump erased anything positive about the legacy of the interregnum president, Joe Biden. “Que sigue la continuidad” (follow the continuity) is the inept slogan of a local politician in the village in Chiapas where family responsibilities have placed me for a few months, but it could well have been the title of Trump’s work plan for the day.
I started keeping a list. Eventually, my journalist brain took over. I had to make choices and prioritize.
The one specific action that I expected with dread came in the evening: revocation of Biden’s announcement six days earlier that some of the cruel U.S. sanctions levelled against Cuba would be eased. Cuban President Miguel Diaz-Canel responded on social media late on Monday, calling Trump’s decision to revoke Biden’s measures an “act of mockery and abuse.”
Here’s my list, drawn partly from Associated Press and the Toronto Star, with additional sources as noted below. At the end, a treat: an eloquent plea for mercy spoken in Trump’s presence by Washington’s Episcopal bishop, the Right Rev. Mariann Edgar Budde.
Trump suspends U.S. foreign aid for 90 days pending reviews
Because this blog is broadly about issues related to development, let me start here: Trump temporarily suspended all U.S. foreign assistance programs for 90 days pending reviews to determine whether they are aligned with his policy goals. (From other statements, it’s pretty clear he is going after support for women’s sexual and reproductive health.) It was not immediately clear how much assistance can be affected by the order. Funding for many programs has already been appropriated by Congress and must be spent. And there are contracts that must be honoured.

Trump declares a border emergency
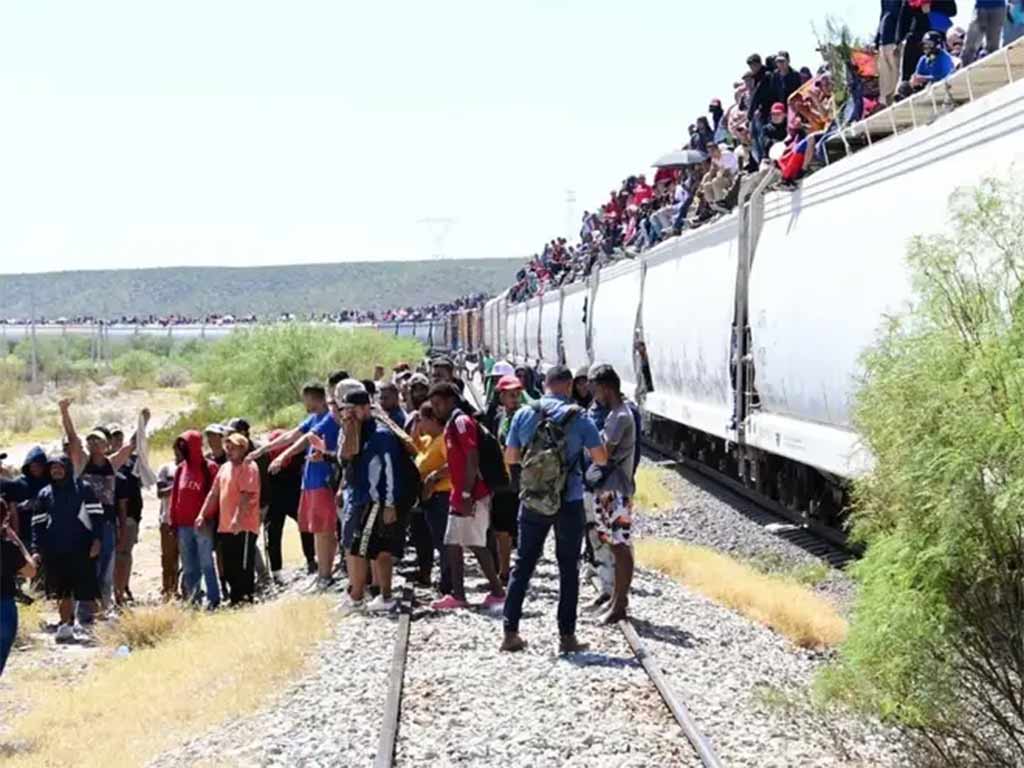
As he had promised, Trump declared a national emergency on the U.S.-Mexico border, suspending refugee resettlement and ending automatic citizenship for anyone born in the U.S. La Jornada reported that he suspended the U.S. government’s CBP One app that asylum-seekers waiting in Mexico use to make appointments for their claim to be heard by officials on the U.S. side of the border.
Trump acknowledged an imminent legal challenge to overturning birthright citizenship, which has been enshrined in the U.S. Constitution since 1868. He said automatic citizenship was “just ridiculous” and that he believes he was on “good (legal) ground” to change it.
Rainbow Railroad newsletter, Jan. 21: Trump signed an executive order that suspended the U.S. Refugee Admission Program, halting the processing of LGBTQI+ refugees already approved for resettlement, and leaving vulnerable and displaced queer and trans individuals stranded in dangerous and precarious conditions.
Use of wartime power act to deport gang members
Trump raised the possibility of using the Alien Enemies Act of 1798 (last used during World War II to detain Japanese people) to deport gang members who are deemed members of a foreign terrorist organization. His executive order paves the way for criminal organizations such as MS-13 to be named “foreign terrorist organizations.” His government will also return “millions of foreign criminals” to their places of origin.

Ending protection from discrimination based on gender identity or sexual orientation
Trump rescinded a 2021 order (Title IX) that the Education Department used to protect against discrimination based on gender identity or sexual orientation.
A couple of paragraphs from the Rolling Stone’s excellent coverage:
Earlier in the day, Trump declared in his inaugural address: “As of today It will henceforth be the official policy of the United States government that there are only two genders, male and female.”
Trump intends to sign an executive order that prohibits federal recognition of transgender Americans. The anticipated order, leaked to the right-leaning Free Press, will reportedly bar government issued identification like passports from listing anything other than a person’s birth gender, remove transgender individuals from protection of laws barring sex-discrimination, end funding for transition surgeries for federal prisoners, and purport to protect the First Amendment and other rights of those who flout “preferred pronouns” or refuse to recognize the reality of transgender individuals.
In addition to a federal hiring freeze, other measures include:
- Pardons and commutations that Trump said would cover about 1,500 people criminally charged in the attack on the Capitol on Jan. 6, 2021
- Halting 78 Biden-era executive actions
- A regulatory freeze preventing bureaucrats from issuing regulations until the Trump administration has full control of the government
- A freeze on all federal hiring except for military and a few other essential areas
- A requirement that federal workers return to full-time in-person work
- A directive to every department and agency to address the cost of living crisis
- Withdrawal from the Paris climate treaty as Los Angeles burns [Canada’s environment minister Steven Guilbeault called the move “deplorable”]
- Withdrawal from the World Health Organization (WHO)
- A government order restoring freedom of speech and preventing censorship of free speech
- Ending the “weaponization of government against the political adversaries of the previous administration”
Episcopal bishop asks Trump ‘to have mercy’ on LGBTQ+ communities and immigrants
video
Washington’s Episcopal bishop, the Right Rev. Mariann Edgar Budde:
“Let me make one final plea, Mr. President. Millions have put their trust in you, and as you told the nation yesterday, you have felt the providential hand of a loving God. In the name of our God, I ask you to have mercy upon the people in our country who are scared now. There are gay, lesbian, and transgender children in Democratic, Republican, and independent families, some who fear for their lives. The people who pick our crops and clean our office buildings, who labor in poultry farms and meatpacking plants, who wash the dishes after we eat in restaurants and work the night shifts in hospitals, they may not be citizens or have the proper documentation, but the vast majority of immigrants are not criminals. They pay taxes and are good neighbors. They are faithful members of our churches and mosques, synagogues, gurdwara, and temples.
I ask you to have mercy, Mr. President, on those in our communities whose children fear their parents will be taken away, and that you help those who are fleeing war zones and persecution in their own lands to find compassion and welcome here. Our God teaches us that we are to be merciful to the stranger, for we were all once strangers in this land. May God grant us the strength and courage to honor the dignity of every human being, to speak the truth to one another in love, and walk humbly with each other and our God, for the good of all people, the good of all people in this nation and the world. Amen.”
A day later, Trump called the bishop a “Radical Left hard line Trump hater,” “ungracious,” “nasty” and “not compelling or smart.”






