by Jim Hodgson
Back on launch day of Trump 2.0, the president issued an executive order that suspended international aid programs for 90 days, including those of the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID).
The move came with a lot of over-the-top rhetoric and outright lies: that USAID spent “$100 million on condoms to Hamas” and that it “bankrolled” the Politico digital news company. “It’s been run by a bunch of radical lunatics. And we’re getting them out,” Trump told reporters on the evening of Feb. 2.
There are, of course, dozens of issues about which to criticize the Trump regime. But this is a blog that sets out to unwrap development issues, so let’s get into it.
Congress established USAID in 1961 to bring together programs that were administering foreign aid. Focusing on long-term social and economic development, USAID disbursed about $72 billion in 2023, less than 1% of the U.S. annual budget. It is one of the largest aid agencies in the world.
You’ll remember, of course, that the United Nations target for spending on Official Development Assistance is 0.7 per cent of gross domestic product. Only five countries meet or exceed that goal: Norway, Luxembourg, Sweden, Germany and Denmark. In 2023, Canada contributed 0.37 per cent of GDP; the United States contributed just 0.24 per cent, seventh lowest among 31 OECD countries.
Trump’s order, carried out by his government efficiency hatchet-man, Elon Musk, chopped humanitarian programs around the world: famine relief in war zones; programs to stall malaria in 22 African nations; vaccinations in vulnerable areas; and access to medications by people living with HIV and AIDS. Several U.S. government websites also removed resources on HIV. (That also happened when Trump first took office in 2017).

In days since the order, enough voices were raised in alarm to get funding for HIV and other essential medicines restored—though it wasn’t clear if that included preventative drugs like PrEP. For more than 20 years, PEPFAR (the President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief) worked within and alongside the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, TB and Malaria and the Joint United Nations Program on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS).
Also, a federal judge on Feb. 7 temporarily blocked the administration from placing 2,200 USAID employees on paid leave, siding with workers who argued Trump and Musk lack the authority to immediately dismantle an agency created by congressional legislation.
The Trump regime blames “migrants” for much of what supposedly ails the United States, but in this time of unparalleled worldwide migration of people, the USAID cuts hit the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees and the International Organization for Migration (IOM)—two agencies that are critical in managing and measuring the flows of people.
No one should argue against humanitarian aid, although Musk and Republican members of congress who see empathy as a character flaw will do so. In a world still suffering from massive inequality, such aid is urgently needed. The U.S. Christian magazine Sojourners offered a strong defence of the humanitarian work of USAID.
What happens after the 90-day review? My guess is that some functions will be folded into the State Department and thus more susceptible to narrow political goals, like subversion of other countries’ governments. I feel badly for beneficiaries of the humanitarian programs and for many well-intentioned employees; not so much for the vast array of U.S.-based independent contractors who get rich from the misery of others.
Sheinbaum: “It’s better they close it”
As noted above, USAID was created in 1961—just two years after the triumph of the Cuban Revolution. There was no artifice: USAID was to counter the influence of Soviet Union. In recent years, USAID has been at the heart of U.S. challenges to the growing influence of China, which has a successful “Belt and Road” foreign aid program of its own.
My venerable Mac laptop computer tells me that I have 226 files that mention USAID. Almost all of the documents are about the ways that USAID is used as an instrument of U.S. foreign policy, especially its work alongside other U.S. institutions that promote—or subvert—democracy in other countries: the National Endowment for Democracy (NED), the International Republican Institute, the National Democratic Institute for International Affairs and even the Central Intelligence Agency.
USAID even had an Office of Transition Initiatives (OTI) that gained infamy in 2014 over its covert “Cuban Twitter” (ZunZuneo) social media program that was aimed at overthrowing the Cuban government was revealed by Associated Press.
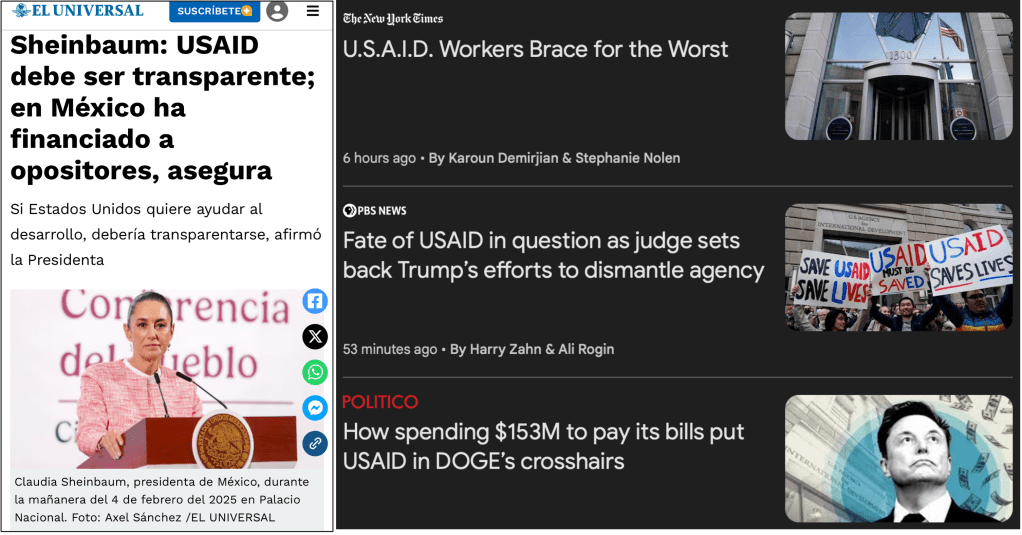
In her morning news conference on Feb. 4, Mexican President Claudia Sheinbaum, breaking away from the dispute over tariffs, lashed out at the overt political activity of USAID. “This agency has funded research projects and groups opposed to the government. That’s the case with Mexico.”
She mentioned an organization that she called, “Mexicans for Corruption.” (She was only half-joking: it’s Mexicans against Corruption. The group actively opposed her predecessor Andrés Manuel López Obrador’s effort to reform the judicial system, and it had support from USAID.)
“And how is it that they get involved in politics, those agencies that are about aid. In that sense, if the United States wants to help with development, it should be transparent,” she continued. “The truth is that there are so many things USAID does that in truth it is better they close it.”
In a similar vein, Colombian President Gustavo Petro said some U.S. help is not welcome and has to go. “Hundreds of immigration officials who guard our borders were paid by the United States. This aid is poison,” he said during a Feb. 3 cabinet meeting. “That should never be allowed. We are going to pay with our money.” In 2024, the agency paid nearly $385 million to Colombia.
Haïti chérie
Which brings me to Haiti, a country whose heartbreak I know well. For more than 45 years, it has been particularly afflicted by HIV and AIDS. The ongoing political crisis, worsened by uncontrolled activity by criminal gangs, continues to hamper relief efforts including support to people living with HIV and AIDS.
Repeated U.S. interventions have made things worse. From 2011, with the presidencies of Michel Martellyand Jovenel Moïse and then the unelected leadership of Prime Minister Ariel Henry through early 2024, the United States and the local elites had the leaders they wanted: men close to the business sector who had close ties in the United States.
That fruitless model was finally shoved aside last June 11 with the installation of a transitional council (CPT). It’s wobbly but hope persists that it can finally organize new elections that produce leaders that Haitians want. A truth commission and an electoral council have been named.
In the meantime, the problem of gang violence is being addressed (though ineffectively) with the addition of the Multinational Security Support Mission (known as MMAS), led by police from Kenya and bolstered with police from El Salvador and Guatemala. Despite UN backing and many promises, it is underfunded and understaffed.

A new blow came Feb. 4 when the UN announced that the shutdown of USAID meant funds for the MMAS were frozen. But two days later, U.S. Secretary of State Marco Rubio announced that MMAS would be protected despite the USAID cut, adding to speculation that Rubio, Musk and Trump are not all operating from the same playbook.
In the wake of the axing of USAID, the best piece that I have read about its activities in Haiti is by a long-time observer, Jake Johnston of the Center for Economic Policy and Research (CEPR). At the end of a Feb. 4 essay about the agency’s work in Haiti, he writes:
The term “aid” encompasses many different things: humanitarian assistance and development programming, contracts and grants, support to local organizations and multimillion dollar contracts to DC-area firms.
There are many parts of the US foreign aid industry that can and should be stopped or significantly reformed. But that doesn’t mean that shutting down USAID, or making its assistance even more overtly political by placing it under the umbrella of the State Department, is going to be a good thing, either in the short or long term.
The reality is that, where foreign assistance is least effective, it is largely because it is designed to promote US interests rather than address the needs of those ostensibly on the receiving end. The changes announced by the Trump administration are not likely to truly disrupt US soft power abroad. If anything, it will make political interventionism an even more explicit aim of US foreign assistance.