A two-day meeting this week in the Colombian capital ended with renewed commitment to pursue accountability for Israeli abuses in Gaza, including by preventing the transfer of weapons to Israel.
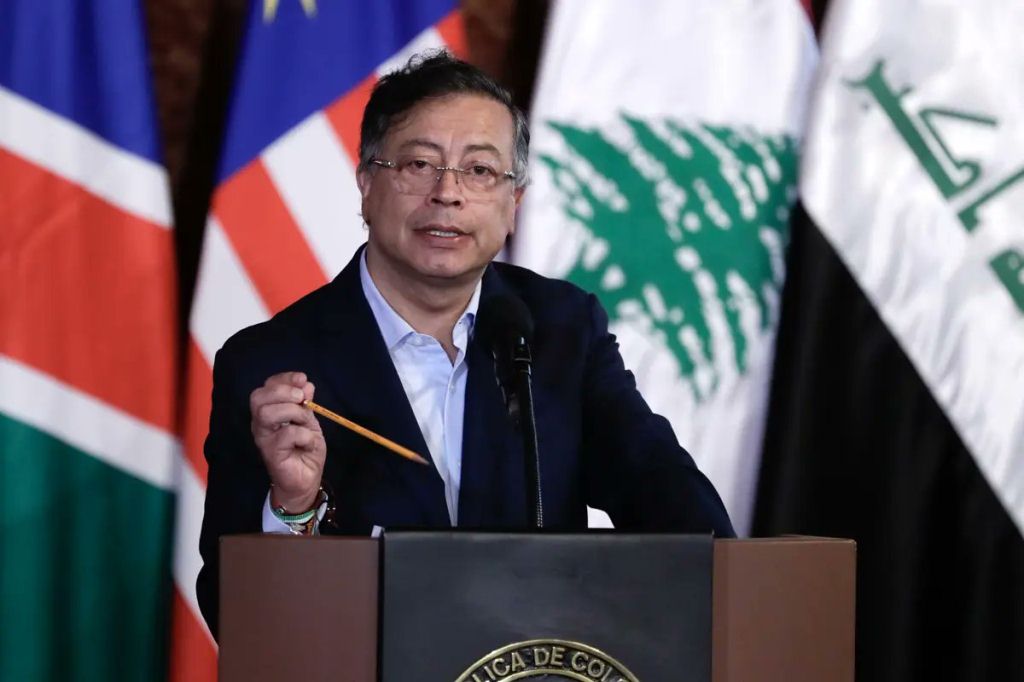

As the event drew to a close Wednesday (July 16), Colombian President Gustavo Petro (above) told participants, “Gaza is simply an experiment by the ultra-rich to show the impoverished people of the world how they will respond to humanity’s rebellion.”
Petro also distanced himself further from the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), which in 2022 had designated Colombia as a “non-member strategic ally.”
“What are we doing in NATO, if its principal leaders are with the genocide?” he asked. “We must leave.”
A coalition known as The Hague Group organised the summit. It was born in January last year through the help of Progressive International (PI), an organization founded in 2020 to unite, organize, and mobilize progressive forces around the world. PI called the Bogotá meeting the “most ambitious multilateral action since the start of Gaza genocide 21 months ago.”
Jointly convened by the governments of Colombia and South Africa as co-chairs, the Hague Group also includes Bolivia, Cuba, Indonesia, Iraq, Libya, Malaysia, Namibia, Nicaragua, Oman and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. At least 18 other countries, plus the United Nations and the World Council of Churches, sent representatives. Qatar and Egypt, which are overseeing negotiations between Hamas and the Israeli government, attended.
During Tuesday morning’s opening event, various officials spoke, calling for an end to Israel’s attacks on Gaza. Colombia’s foreign minister, Rosa Yolanda Villavicencio, said during her morning address that Israel’s attacks constitute an unequivocal “genocide.”
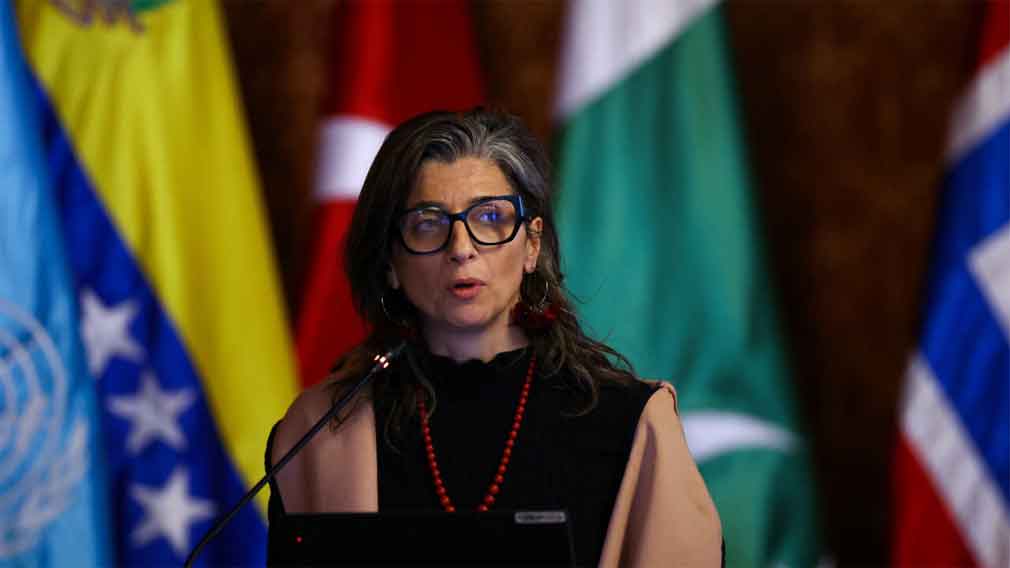

Another key participant was Francesca Albanese (above), the U.N. special rapporteur for the Palestinian Territories. She denounced the inaction of the international community. She accused the West of justifying Israeli actions as the “right to defense” and said the vetos in the U.N. Security Council “protect war crimes” carried out in the sight of all.
“Palestine has changed global consciousness, drawing a clear line between those who oppose genocide and those who accept it or are part of it,” she said. Albanese was recently sanctioned by the US for her outspoken criticism of Israel’s actions.
“We believe in protagonism, not supplication,” said Varsha Gandikota-Nellutla, the executive secretary of The Hague Group. “Today marks an end to the era of the impunity and the beginning of collective state action by governments of conscience.”
The group members committed to implementing six measures immediately through their domestic legal and administrative systems to break the ties of complicity with Israel’s campaign of devastation in Palestine. They set September 20 as a date for other states to join them, coinciding with the 80th U.N. General Assembly. Consultations with capitals across the world are now ongoing.
“We hereby announce the following measures,” the Joint Statement on the Conclusion of the Emergency Ministerial Conference on Palestine reads, “to be adopted based on states’ domestic legal and legislative frameworks:”
- Prevent the provision or transfer of arms, munitions, military fuel, related military equipment, and dual-use items to Israel…
- Prevent the transit, docking, and servicing of vessels at any port…. in all cases where there is a clear risk of the vessel being used to carry arms, munitions, military fuel, related military equipment, and dual-use items to Israel
- Prevent the carriage of arms, munitions, military fuel, related military equipment, and dual-use items to Israel on vessels bearing our flag… and ensure full accountability, including de-flagging, for non-compliance with this prohibition.
- Commence an urgent review of all public contracts, to prevent public institutions and funds from supporting Israel’s illegal occupation of the Palestinian Territory and entrenching its unlawful presence.
- Comply with obligations to ensure accountability for the most serious crimes under international law, through robust, impartial and independent investigations and prosecutions at national or international levels, to ensure justice for all victims and the prevention of future crimes.
- Support universal jurisdiction mandates, as and where applicable in national legal frameworks and judiciaries, to ensure justice for victims of international crimes committed in the Occupied Palestinian Territory.
“These 12 states have taken a momentous step forward,” said Albanese about the joint statement. “The clock is now ticking for states—from Europe to the Arab world and beyond—to join them.”
The full joint statement is here.
Complete text of Albanese’s remarks is here.






